OBJECTIVE: This study aims to evaluate the effectiveness and tolerability of a phytotherapeutic topical gel (Douloff®) compared to oral paracetamol for acute pain resulting from minor limb soft tissue injuries.
METHODS: A prospective, multicenter, randomized, double-blind study conducted over 13 months in three EDs. Patients aged 18 years and older, with minor limb soft tissue injuries, were randomized into Douloff® (n = 765) and paracetamol (n = 750) groups. The primary outcome was the pain resolution rate (reduction of at least 50% of pain intensity, measured by the numeric rating scale (NRS) on active motion at day-7compared to NRS at discharge). Secondary outcomes included time to pain resolution, rescue analgesia, patient satisfaction and adverse events.
RESULTS: The groups were comparable in terms of baseline characteristics. On day-7, resolution of pain was observed in 641 patients (83.7%) in Douloff® group versus 535 patients (71.3%) in paracetamol group (OR 1.27; 95% CI 1.015-1.6; p = 0.02). Median time to reach pain resolution was 4.5 ± 2.9 days in Douloff® group compared with 5.6 ± 3.3 days in paracetamol group (p < 0.001). Patients in Douloff® group required less rescue analgesics (48.2%) compared to paracetamol group (59.1%) (-10.9%, 95% CI -15.89 to -5.9; p < 0.001). No major adverse events were observed in either group, and 89.4% of patients in Douloff® group were satisfied, compared to 92.5% in the paracetamol group (p < 0.001).
CONCLUSION: Douloff®, a topical herbal paste, is superior to oral paracetamol in the management of acute pain related to soft tissue injuries. It can be considered as an alternative to conventional analgesics.
| Discipline Area | Score |
|---|---|
| Physician | 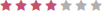 |
Physician rater
Hard to know what to do with the results of an unblinded study of this nature. This is unlikely to impact emergency medicine practice.
Physician rater
A combination of essential oils seems to be better than oral paracetamol in patients with non-fracture, acute soft tissue traumatic injury. While this is welcome news that other modalities of pain control can be effective, the exact formula used won't be commonly available outside of Tunisia (the study country). However even arbitrary use of some essential oils may be beneficial, and without harm, as part of a multi-modal treatment for pain. Although there are limitations as stated in the study as well as potential imbalance from the types of injuries, it seems reasonable that some of the essential oils that were used be considered for pain relief in patients who are looking for alternatives to paracetamol or NSAIDs.





 , McMaster University
, McMaster University