BACKGROUND: This network meta-analysis (NMA) aimed to explore the impact of Non-pharmacological therapies (NPT) on alleviating primary dysmenorrhea (PD) symptoms and assess the effectiveness differences among various NPT.
METHODS: We searched seven databases and summarized clinical trials of PD treated with NPT from inception to September 6, 2023. Randomized controlled clinical trials (RCTs) of PD treated with NPT. The outcomes were the Visual Analog Scale (VAS), the Cox menstrual symptom scale (CMSS), and response rate. Quality was assessed using the Cochrane risk of bias assessment tool. Pairwise meta-analysis and network meta-analysis (NMA) was performed by RevMan (5.4), Stata (15.0), and WinBUGS (1.4.3). The ranking probabilities for all treatment interventions were performed using the Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking curve (SUCRA).
RESULTS: A total of 16 RCTs were finally included, involving 8 kinds of NPT. Results of pairwise meta-analyses: For the VAS score results, moxibustion (SMD: -0.591,95% CI: -0.916, -0.266) was more effective than acupuncture, acupuncture (SMD: -0.948,95% CI: -1.853, -0.044) was more effective than placebo, and yoga (SMD: 2.634,95% CI: -4.28, -0.988) was more effective than the blank control. NMA results: Compared to the blank control, acupuncture (SMD: -4.81; 95% CI: -6.63, -3.00), auricular point therapy (SMD: -4.36; 95% CI: -7.18, -1.60), yoga (SMD: -2.12; 95% CI: -3.13, -1.09), moxibustion (SMD:5.54; 95% CI: 3.33, 7.68), and placebo (SMD: 3.10; 95% CI: 1.03, 5.27) proved to be a superior reduction in VAS. The use of acupressure (SMD: 2.49; 95% CI: 0.03, 5.03), moxibustion (SMD: -2.45; 95% CI: -4.06, -0.71), and acupuncture (SMD: -1.72; 95% CI: -2.75, -0.56) demonstrated a greater decrease in VAS efficacy than placebo. The consolidated ranking outcomes indicate that moxibustion, acupuncture, and auricular acupoint therapy occupy high SUCRA positions across various outcome metrics.
CONCLUSION: Acupuncture, moxibustion and auricular point may be the best treatment for PD. In the future, more trials are needed to obtain higher-quality evidence and the best protocols.
| Discipline Area | Score |
|---|---|
| Physician | 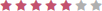 |
Physician rater
This article is very useful for gynecologists in their daily routine practice for managing primary dysmenorrhea (PD). Recent studies suggest that non-pharmacological therapies are viable and effective treatment options for women with PD, particularly for those unsuitable for pharmacological therapies (oral contraceptives or nonsteroidial anti-inflammatory drugs). This evidence suggests that compared with placebo and no treatment, non-pharmacological therapy can reduce the severity of primary dysmenorrhea in patients. Among them, acupuncture, moxibustion, and auricular point therapy may be the best treatment, or the first-line therapy, for improving symptoms associated with primary dysmenorrhea. Further analysis in this area should be continued. Future large well-designed RCTs, extensive follow-up, and better methodological quality are needed in the future to summarize and update the results of this study.
Physician rater
Interesting article. Some of these options are cost prohibitive, not readily available, and/or not widely known. I will need to look more into some of these treatment options.





 , McMaster University
, McMaster University