OBJECTIVE: Migraine is a common neurological disorder, which resulting in significant societal and personal burdens. Acupuncture has attracted widespread attention in migraine prophylaxis and treatment in recent years. Although some studies have confirmed the effectiveness of acupuncture therapy in treating migraines, there is still a lack of comprehensive evaluation regarding the comparison between different types of migraines and various acupuncture therapies. Furthermore, certain special acupuncture methods have not received sufficient attention and research. Therefore, the objective of this study is to summarize and expand upon previous research, update existing evidence, and compare the efficacy of different acupuncture therapies for migraine. We aim to provide stronger evidence-based support for clinical practice through this study, thereby promoting wider application of acupuncture therapy in migraine treatment.
METHODS: A exhaustive and methodical search was conducted across the nine databases: PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, Scopus, the Cochrane Library, CBM, CNKI, WANFANG and VIP Data. The Visual Analog Scale (VAS) scores, migraine attack frequency, duration, days of attack and adverse effects were observation indicators.
RESULTS: This study included 34 studies involving a total of 3365 migraineurs. The results of the study demonstrated that acupuncture therapy reduced VAS scores of migraine patients better compared to medication (MD=-1.29, 95% CI=[-1.67,-0.92]) and exhibited greater efficacy in reducing the frequency of migraine attacks (MD=-1.95, 95% CI=[-3.06,-0.85]), the duration of attacks (MD=- 3.29, 95% CI=[-4.65,-1.93]), and days of attack (MD=-1.02, 95% CI=[-1.58,-0.47]). Significant heterogeneity suggested that different acupuncture therapies had varying effects, and that the efficacy of the same therapy may also vary in different migraine types. In the context of network meta-analysis, the SUCRA of acupuncture therapies for reducing VAS scores was ranked as special acupuncture method (98.3%), acupuncture plus medicine (71.9%), and acupuncture (54.5%). Blood-letting and cupping was the most effective treatment for lowering the frequency of migraine attacks. The most effective treatment for shortening the duration of migraine was acupuncture plus medication (81.2%). When it comes to decreasing the days of migraine, acupuncture (80.3%) came out on top. 14 studies reported the occurrence of adverse effects, of which 4 studies had no adverse effects in the test group.
CONCLUSION: Initial findings indicate that acupuncture-related therapy exhibits superior effectiveness in the treatment of migraine and clinical decision-making should be patient-specific.
| Discipline Area | Score |
|---|---|
| Rehab Clinician (OT/PT) | 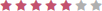 |
| Physician |  |
Physician rater
Previous studies have supported acupuncture for migraines. This meta-analysis contains similar limitations (i.e., a lack of blinding to the treatment group). Most studies used a drug for a control group. The potential expectations of benefit for acupuncture, cupping, or bloodletting among participants creates potential bias.





 , McMaster University
, McMaster University